In recent years, drone delivery has evolved from an ambitious concept to a real-world solution for last-mile logistics. From delivering medicines in remote villages to fulfilling e-commerce orders in suburban neighborhoods, drones are changing how we think about speed, accessibility, and automation in logistics. But how do automated drone delivery systems actually work?
What Is an Automated Drone Delivery System?
An automated drone delivery system is an integrated network of software, hardware, and infrastructure that allows unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to deliver packages with minimal or no human intervention. These systems combine advanced robotics, navigation algorithms, and communication protocols to handle everything from route planning to real-time decision-making.
Unlike manual or semi-automated drone flights, these systems can manage multiple deliveries across various geographies autonomously, thanks to the synergy of technologies such as computer vision, edge computing, and fleet orchestration platforms.
Components of a Drone Delivery System
Aerial Hardware (The Drone Itself)
Every delivery system starts with the drone. Most delivery drones are electric, equipped with GPS, inertial navigation systems, onboard processors, and a payload mechanism (like a winch, container, or drop-door). Modern drones also include obstacle avoidance sensors (LiDAR, ultrasonic, optical flow) and redundant flight controllers for safety.
Key specs typically include:
- Payload capacity (e.g., 2–10 kg)
- Flight range (usually 10–25 km)
- Battery life (20–45 minutes)
- VTOL or hybrid takeoff and landing capabilities
Onboard Autonomy
Autonomous drones must perceive, process, and act in real-time. Onboard autonomy includes:
- Obstacle detection and avoidance
- Dynamic flight adjustment
- Emergency landing protocols
- Payload release mechanisms
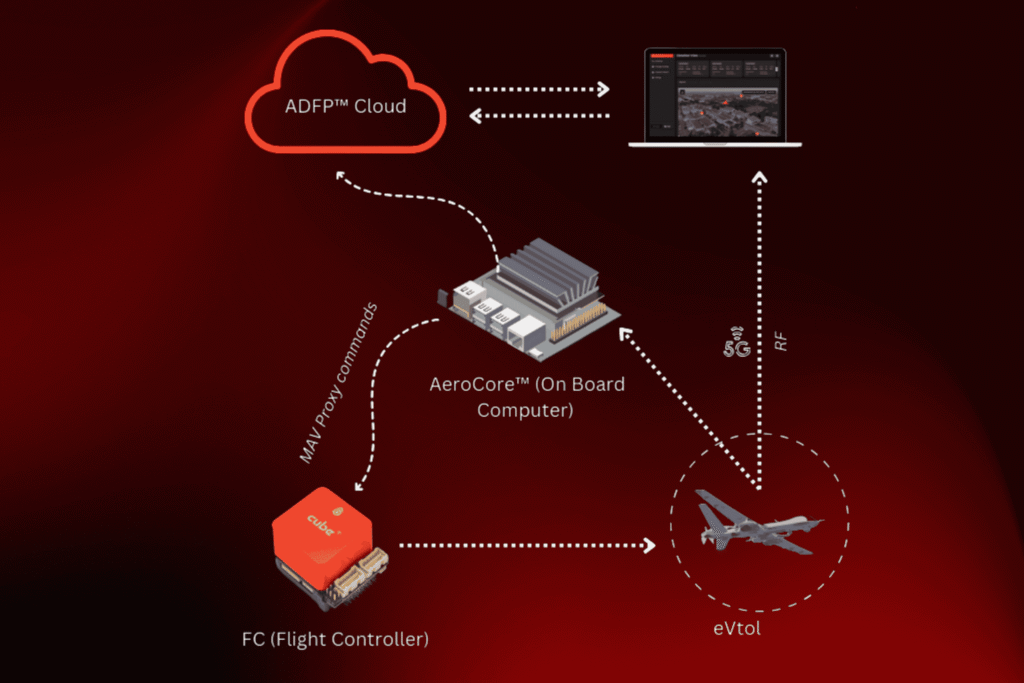
This processing often happens via edge computing, reducing latency and improving decision speed without relying heavily on remote servers.
Navigation and Routing Algorithms
Navigation is a critical part of drone autonomy. The system must plan the most efficient, safe, and compliant route from the point of dispatch to the delivery location. Route planning uses:
- GPS + RTK for centimeter-level accuracy
- Airspace maps for no-fly zones and altitude restrictions
- Dynamic rerouting in case of obstacles, weather, or air traffic
- Geofencing to enforce invisible boundaries around delivery sites or restricted areas
In urban drone delivery, vertical routing and 3D mapping help drones navigate between buildings or land on designated rooftops or drone ports.

Communication and Control Systems
Despite the autonomy, drone delivery systems need continuous communication with ground stations and fleet management software.
Key communication methods include:
- 4G/5G cellular for live telemetry and video feed
- Radio frequency (RF) for backup control
- LoRa or mesh networks in remote areas
- Satellite connectivity (in limited use cases)
Real-time telemetry allows operators to monitor location, speed, altitude, battery status, and system health. For fully autonomous missions, this telemetry is also fed to backend systems that apply rules, update schedules, or trigger alerts when anomalies occur.
Delivery Mechanism and Drop Safety
The method of releasing a package is a critical design decision. Safe delivery without damaging the item or injuring people requires precision.
Common methods include:
- Winch-drop systems (lower the package via cable)
- Hatch-door or belly-drop systems
- Hover-and-release over designated landing zones
- Hand-off to ground-based robotics (in advanced systems)
Drop safety is managed using altimeters, vision systems, and ground validation (e.g., QR codes, smartphone confirmation, or weight sensors).
Ground Infrastructure and Charging
For large-scale drone operations, a network of ground stations is essential. These hubs act as launching pads, charging stations, and maintenance depots.
Features of drone delivery ground infrastructure:
- Automated battery swapping or rapid charging
- Parcel loading/unloading bays
- Weather-proof drone enclosures
- Edge servers for local data processing
Such infrastructure ensures high uptime and scalable deployment in suburban and rural zones.
Fleet Management and Orchestration Software
To scale beyond one or two drones, companies rely on sophisticated fleet management software. This platform is the brain that orchestrates:
- Mission scheduling and coordination
- Airspace deconfliction
- Performance monitoring
- Maintenance alerts and predictive analytics
These platforms often integrate with regulatory bodies through UTM (Unmanned Traffic Management) systems, enabling safe and legal flight paths in shared airspace.
Safety and Compliance
Safety and compliance are non-negotiable in automated drone logistics. Systems are designed to follow aviation regulations such as:
- BVLOS (Beyond Visual Line of Sight) permissions
- ADS-B In/Out for air traffic awareness
- Failsafe return-to-home (RTH) protocols
- Weather and wind resistance limits
- Pilot in command (PIC) oversight, if required
Flight logs, incident reports, and audit trails are automatically generated to meet compliance in real-time.
The Role of AI in Drone Delivery
Artificial intelligence amplifies the intelligence of autonomous drones through:
- Visual recognition of landmarks, landing zones, and obstacles
- Predictive battery and motor health monitoring
- Learning optimal flight routes based on historical data
- Anomaly detection in telemetry or mission execution
AI is also used in last-mile decisions, like when to delay a delivery due to unexpected human activity near the drop zone.
Real-World Applications
Automated drone delivery is already making an impact in areas such as:
- Medical supply drops in remote or disaster-hit areas
- Food and grocery delivery in suburban neighborhoods
- E-commerce logistics for rapid last-mile fulfillment
- Agricultural supply chain logistics in rural farming zones
As regulatory frameworks evolve and hardware becomes more affordable, more industries will leverage these systems to cut delivery times, costs, and environmental impact.
Taking Flight Into the Future
Automated drone delivery systems are not a distant dream—they are a rapidly evolving reality. With advances in autonomous navigation, edge AI, cloud integration, and safety protocols, drones are poised to transform the way we think about logistics and accessibility.
Whether it’s delivering critical medicine or your next online purchase, drones are shaping a future that’s faster, safer, and more connected from the skies.