What’s next for automated logistics in the sky?
Just a few years ago, the idea of drones delivering groceries, medicine, or online orders felt like a far-off dream. Today, it’s already happening in several countries. But we’re only scratching the surface.
As demand for fast, contactless, and scalable delivery continues to grow, the drone delivery industry is evolving rapidly—powered by breakthroughs that go far beyond GPS and battery life. In this article, we explore the emerging technologies that are quietly but powerfully shaping the next generation of drone delivery systems.
AI-Driven Airspace Management
As more drones take to the skies, airspace will get crowded—especially in urban environments. The traditional method of flight planning won’t scale. That’s where AI-powered airspace management systems come in.
These systems use real-time data and machine learning to:
- Predict traffic congestion in drone corridors
- Avoid mid-air collisions dynamically
- Allocate altitude layers and time slots on the fly
- Automatically comply with changing airspace rules
Example: Companies like Altitude Angel and AirMap are developing real-time UTM (Unmanned Traffic Management) platforms that act like air traffic control—but for autonomous drones. AI helps deconflict hundreds of simultaneous missions over the same region.
Swarm Intelligence and Collaborative Flight
What if dozens—or hundreds—of drones could fly together like a flock of birds, adjusting to one another’s movements without crashing?
That’s the promise of swarm intelligence in drone delivery. Inspired by the collective behavior of insects and birds, this approach allows drones to:
- Share environmental data with nearby units
- Self-organize flight paths
- Cover larger delivery areas cooperatively
- Reduce energy consumption through formation flying
Potential Use Case: In agriculture, swarm drones can deliver pesticides or small parcels across large farms without centralized coordination. In urban areas, coordinated drone fleets could serve apartment complexes more efficiently during peak hours.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells: Beyond Battery Limits
One of the biggest constraints in drone delivery today is battery life. Most commercial drones top out at 20–30 minutes of flight time. But a new generation of drones powered by hydrogen fuel cells promises to break that barrier.
Benefits of hydrogen-powered drones:
- 3x to 5x longer flight times
- Faster refueling compared to recharging batteries
- Lower carbon footprint (with green hydrogen)
- Suitable for long-range or high-payload missions
Real-world development: Companies like Doosan Mobility Innovation and Intelligent Energy are actively testing hydrogen drones for long-haul deliveries and emergency medical logistics.
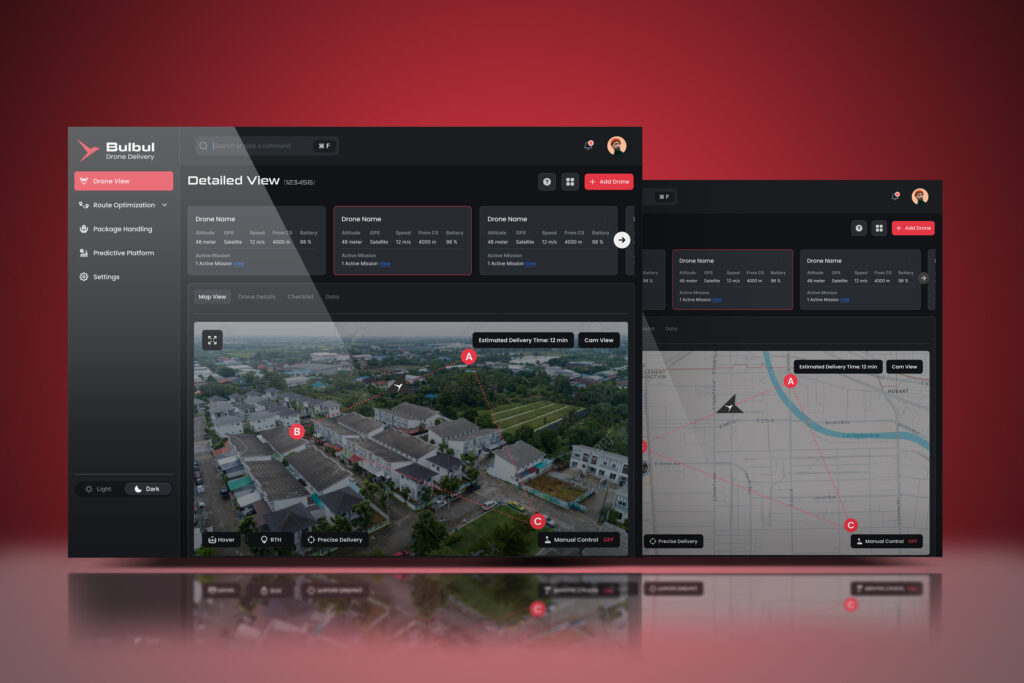
Vision-Based Autonomous Landing
Today’s drones mostly rely on GPS for navigation and delivery. But when it comes to pinpoint landing in GPS-compromised environments—dense cities, indoors, under bridges—vision-based landing systems offer a smarter alternative.
These systems use:
- Downward-facing cameras
- QR-code-like (ARUCO) landing markers
- AI to identify rooftops, balconies, or landing pads
- Computer vision to detect humans or animals near drop zones
Why it matters: For urban drone delivery to scale, drones must land with surgical accuracy on rooftops, balconies, or private driveways—without risking safety or relying solely on satellite data.
Blockchain for Secure Package Tracking
As drone delivery grows, especially for valuable or sensitive items like pharmaceuticals or electronics, security and traceability become critical.
That’s where blockchain steps in. By creating an immutable record of every step—from warehouse dispatch to in-flight telemetry to doorstep delivery—blockchain can:
- Prevent package tampering
- Ensure regulatory compliance (especially for cross-border shipments)
- Create trust with customers and authorities
- Enable real-time audit trails
Use case: In regions with strict chain-of-custody requirements (e.g., for vaccines), blockchain can validate that temperature thresholds and delivery timelines were met—even if the package changed drones mid-route.
Droneports and Rooftop Delivery Infrastructure
While the drones are becoming smarter, the ground infrastructure they rely on is evolving too. The rise of droneports—dedicated hubs for launch, landing, and recharging—is enabling scalable delivery networks.
Features include:
- Automated battery swap systems
- Conveyor integration for sorting parcels
- Modular rooftop stations in cities
- Weatherproof enclosures for 24/7 operation
Example: Skyports in the UK and Urban-Air Port are experimenting with compact, modular droneports designed for integration with buildings, hospitals, and logistics centers.
Predictive Flight Planning Using Real-Time Weather AI
Weather has always been a major disruptor in drone operations. Even light rain or strong gusts can delay missions. But new weather-aware AI systems are making drones smarter about when, where, and how they fly.
These systems combine:
- Hyper-local weather data
- Machine learning models trained on flight logs
- Terrain and wind tunnel simulations
- Forecast-based go/no-go recommendations
Real-world need: In hilly regions or coastal cities, where weather shifts quickly, drones that can self-adjust routes or delay deliveries intelligently will have a significant operational advantage.
Payload Recognition and Adaptive Handling
One emerging trend is the use of computer vision and sensor fusion to recognize different package types and adjust flight behavior accordingly.
This tech allows drones to:
- Balance their load mid-air
- Adjust flight speed or altitude for heavier items
- Verify package ID before release
- Detect tampering or payload failure en route
Why it matters: As drone delivery expands into sectors like cold chain logistics, luxury goods, or perishables, package-specific handling will be a major differentiator for reliability and safety.
Drones-as-a-Service (DaaS) Platforms
Not every business wants to own, operate, and maintain a drone fleet. Enter Drones-as-a-Service, a model where companies subscribe to drone delivery as a utility.
What DaaS offers:
- Fully managed drone missions
- API-based integration with e-commerce and ERP systems
- Pay-per-use pricing
- Compliance and fleet maintenance handled by the provider
Example: Retailers in suburban areas can plug into drone delivery networks via API without investing in hardware or pilot training—much like using AWS for computing power.
The Sky Is Getting Smarter
The future of drone delivery isn’t just about faster drones—it’s about smarter systems. With AI, fuel innovation, swarm coordination, and secure data systems working together, the next decade promises a logistics ecosystem that’s safer, more efficient, and dramatically more scalable.
As regulators, city planners, and tech companies converge on the drone delivery challenge, the sky above us is quickly becoming the next layer of the global supply chain.